Introducing the Shell
The Unix Shell
What is the shell?
The shell (also known as the command-line) is a program that allows us to tell the computer what to do by giving it a “command”.
Tip
Other names for the shell are terminal, Bash, UNIX command line, and more.

Figure 1: Command Line Interface (CLI)
What is the shell?
Another common way we tell the computer what to do is through the use of a “point and click” graphical user interface (GUI) approach.
Figure 2: Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Why use the shell?
Isn’t pointing and clicking easier?
Why use the shell?
Imagine you had the following task:
You have a directory with 10 .txt files.
Pull the first line from each file into a single new file. You should end up with a list of all of the first lines.
Take a look below to see the process for GUI and CLI.
Why use the shell?
Imagine you had the following task:
You have a directory with 10 .txt files.
Pull the first line from each file into a single new file. You should end up with a list of all of the first lines.
Take a look below to see the process for GUI and CLI.
1. Create new file
2. Open file 1, copy line 1, paste into new file, close file 1.
3. Open file 2, copy line 1, paste into new file, close file 2.
4. Repeat 7 more timeshead -n1 -q *.txt > new-file.txtFor this task, the GUI was tedious, time-consuming, and error-prone while the CLI was a single-command, quick, and relatively error proof.
Accessing the Shell
Let’s start using the shell.
Open the shell (terminal) on your computer.
- Go the the Start menu and select “All Apps”.
- Scroll down the list of applications and select the
Gitoption. - From the drop-down menu, select
Git Bash. - A terminal should open up.
- Open Finder and go to the Applications tab.
- Scroll down the list of applications and select
Utilities. - Select
Terminal. - A terminal should open up.
Using the shell
Once we open our terminal, the $ shows us that shell is ready for input.
Using the shell
Let’s see what day it is using the ls command.
lsstands for list- lists the objects in a location
In your terminal, type ls and press enter.
Using the shell
count.sh
example.gtf
exercise-data
fastqc.sh
fastqc_step.sh
feature_counts.sh
index
metadata.txt
north-pacific-gyre
rnaseq
rnaseq.sh
simulated_reads
star.sh
thesis
trim.sh
trim_fq.shBefore we learn more commands, let’s learn about the structure of commands.
Command syntax
Commands follow a general syntax
command option/flag argument
command– the main commandoption/flag– modifies the behavior of the command, often optionalargument– the source and/or target of the command, sometimes optional
Tip
- Options use either
-or--to signal their usage. - Arguments can be either a target (as in the
lscommand) or both a source and target (as in themvcommand)
Command syntax
Let’s change the way ls command behaves by providing a value for the option.
In your terminal, type ls -F and press enter.
Command syntax
count.sh
example.gtf
exercise-data/
fastqc.sh
fastqc_step.sh
feature_counts.sh
index/
metadata.txt
north-pacific-gyre/
rnaseq/
rnaseq.sh
simulated_reads/
star.sh
thesis/
trim.sh
trim_fq.shThis -F option/flag returns the output in a different format, with a / following directories and @ preceeding symbolic links.
Getting help
To better understand command usage and their options we can use the following (depending on the command).
| Method of getting help | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--help or -h option/flag |
Displays help menu for the command/program | ls --help |
man command |
Displays the manual for the command/program in-depth | man ls |
Getting help
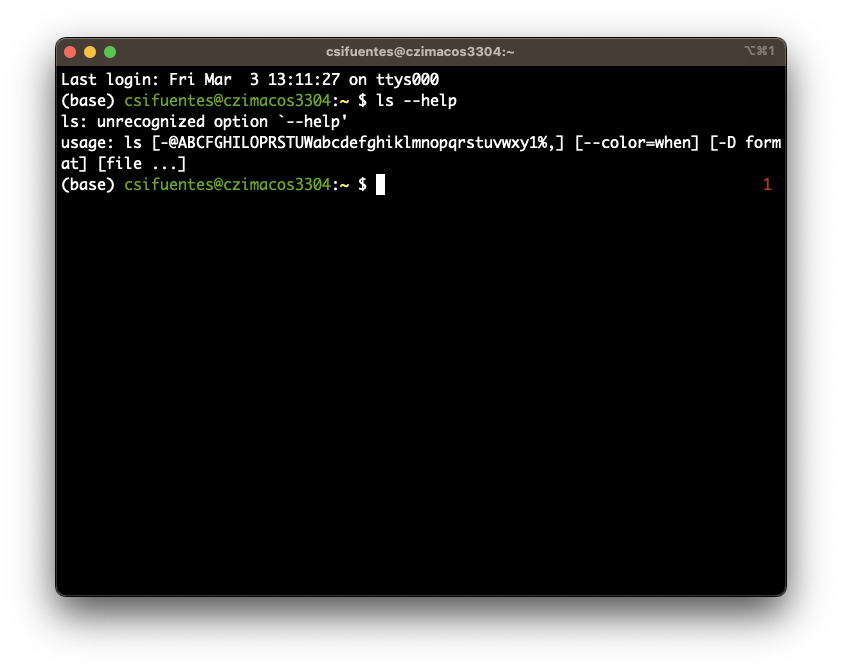
--help flag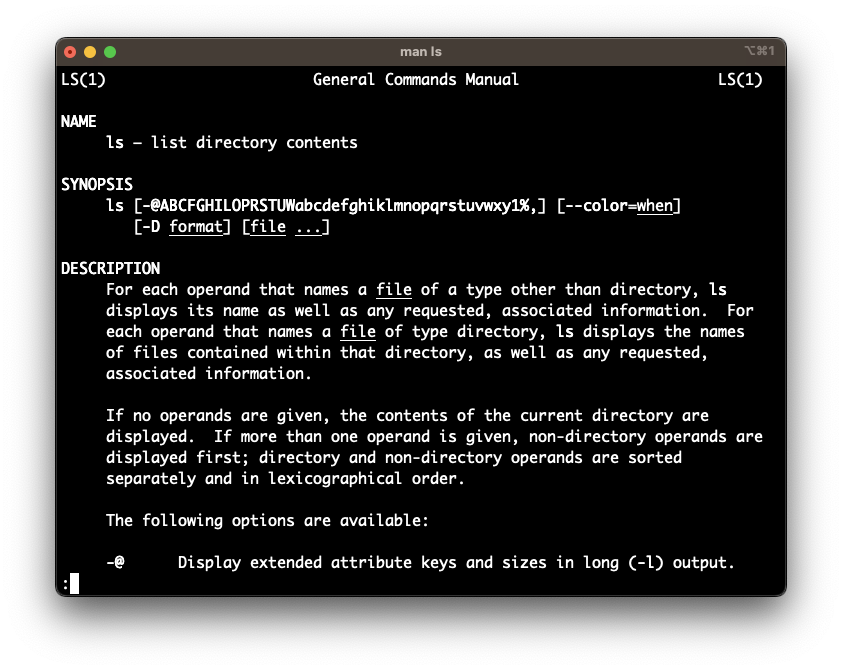
man commandMaking sense of errors
The shell provides (usually) helpful and informative error messages.
Making sense of errors
For example, if you look closely at the ls --help example above, you’ll see that the usage of --help actually resulted in an error (see below).
Q&A: What is the error telling us?
Making sense of errors
Q&A: What is the error above telling us?
Answer
--helpis an unrecognized option
- The correct usage and options for
ls